Thought of the Week – This could become a problem for Europe in 2024
It feels like we have moved on from the inflation shock caused by gas supply disruptions in late 2021 and the Russian invasion of Ukraine in early 2022. The ECB and other European central banks have stopped hiking rates and natural gas prices have declined to lower, though not cheap levels. Yet, a study by two researchers from the Bank of Italy indicates that we may not yet be in the clear.

Piergiorgio Alessandrini and Andrea Giovanni Gazzani used data from 2010 to 2022 to compare the impact of energy price shocks on European economies. Crucially, they found that there is a difference between a supply shock from oil compared to a supply shock from gas.
Obviously, disrupting oil and gas supply are both inflationary in the short run, but the transmission of these shocks into core inflation and economic output is different. This is because oil prices are of lesser importance to European households than gas prices. Unlike in the US where oil is used to fuel cars and also to power industrial facilities, European consumers feel the pinch of higher oil prices at petrol stations, but the pinch from higher gas prices in the form of higher electricity bills, higher gas bills to heat their homes and increased inflation for products that use gas in the manufacturing process. And while higher oil prices are passed through to higher fuel prices at petrol stations almost immediately, the structure of natural gas markets is such that increased wholesale prices take longer to pass through to retail customers.
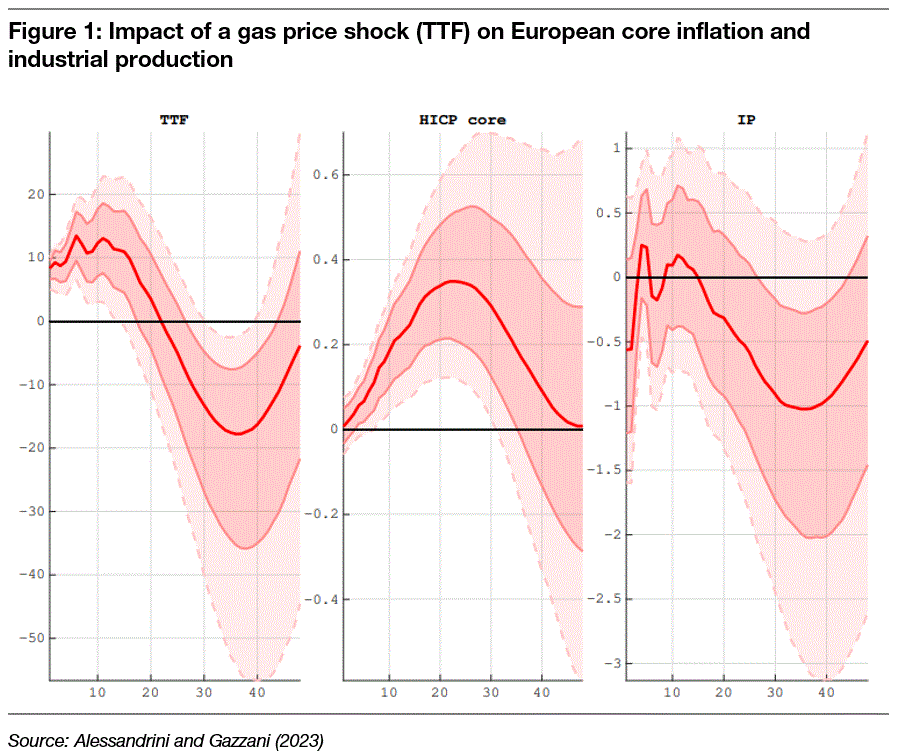
The result is that gas supply shocks take longer to digest and create longer-lasting effects on core inflation and economic output. The chart below shows the model estimates from the study for the reaction of core inflation and industrial production to a shock in natural gas prices (TTF). The shock from higher gas prices takes about 18-24 months to filter through to core inflation, peaking roughly after 20 months. Given that European gas prices started their exponential rise in autumn 2021, this indicates a peak impact on core inflation in summer 2023, and that is about what we have seen this year.
But note that the impact on industrial production is greatest some 30-36 months after the initial gas price shock. This indicates that it will take until spring/summer 2024 before we feel the peak impact of the gas price shock in 2021/22 on the European economy. If this is correct, then the knock-on effects from higher gas prices in Europe and the resulting shock to core inflation and wages will only come through in the next 6-12 months, much later than what we are used to from oil price shocks. This story may not be over, yet.
Thought of the Day features investment-related and economics-related musings that don’t necessarily have anything to do with current markets. They are designed to take a step back and think about the world a little bit differently. Feel free to share these thoughts with your colleagues whenever you find them interesting. If you have colleagues who would like to receive this publication please ask them to send an email to joachim.klement@liberum.com. This publication is free for everyone

